Naomi R.
If you are like most people, your recent healthcare interaction likely involved some sort of medical device or equipment: a blood pressure monitor, a continuous glucose monitor, maybe even an MRI scanner. In fact, a recent Deloitte report states more than 500,000 medical technologies are currently available in the United Kingdom.
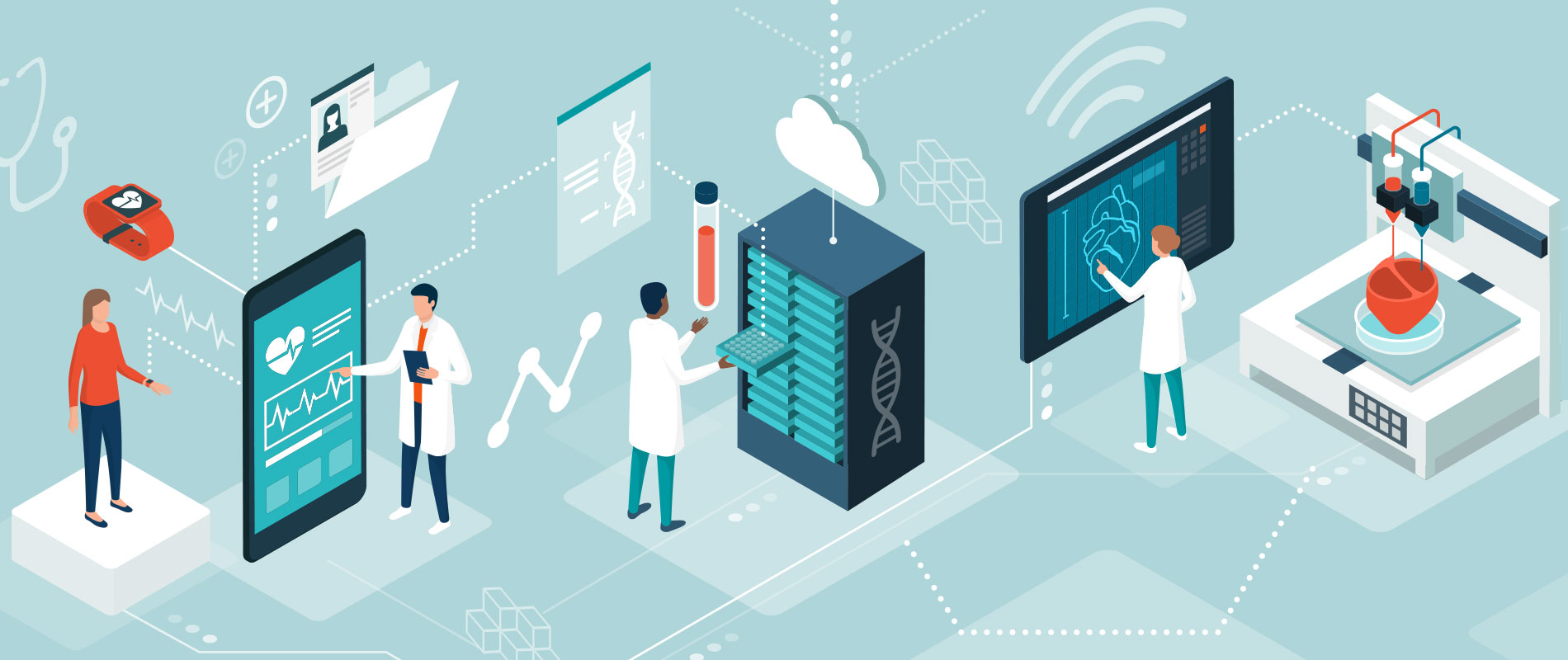
Today’s internet-connected devices are being designed to improve efficiencies, lower care costs, and drive better outcomes in healthcare. As computing power and wireless capabilities improve, organizations are leveraging the potential of technologies on the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
With their ability to collect, analyze, and transmit health data, IoMT tools are rapidly changing healthcare delivery. For patients and clinicians, these applications are playing a central part in tracking and preventing chronic illnesses—and they’re poised to evolve the future of care.
But how exactly does this connected ecosystem work? And what is the real difference between the Internet of Things and IoMT?
What Is IoMT?
The IoMT is a connected infrastructure of medical devices, software applications, and health systems and services.
A growing pool and general adoption of IoT technologies are benefiting many industries. However, what sets the IoMT apart is a wave of sensor-based tools and the marriage of internet-connected medical devices with patient information. This includes wearables and stand-alone devices for remote patient monitoring.
The rise of IoMT is driven by “an increase in the number of connected medical devices that can generate, collect, analyze or transmit health data or images,” the Deloitte report notes. It further states that these devices connect to healthcare provider networks, transmitting data to either internal servers or a cloud repository.
The connectivity between medical devices and sensors streamlines clinical workflow management. It also leads to an overall improvement in patient care, both within care facilities and in remote locations.
The Potential of IoMT in Healthcare
The capabilities of IoMT are more accurate diagnoses, fewer mistakes, and lower costs of care. Paired with smartphone applications, the technology allows patients to send their health information to doctors in order to better surveil diseases and track and prevent chronic illnesses.
Researchers from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and UCLA conducted a study on the Fitbit’s capability to accurately evaluate patients with ischemic heart disease. The wearable device was able to monitor their heart rate and accelerometer data simultaneously. mHealthIntelligence also reports that 88 percent of care providers are investing in remote patient monitoring solutions.
This type of technology is not only helping to improve the patient experience by eliminating the need for in-person medical visits—it’s also helping to reduce costs. Goldman Sachs estimates that IoMT will save the healthcare industry $300 billion annually in expenditures primarily through remote patient monitoring and improved medication adherence.
That said, another positive effect of IoMT is on drug management via the introduction of “smart pills.” These medicines contain microscopic sensors, which, once swallowed, can transmit data to connected devices.
Some digital medicine companies, such as Proteus Discover, have focused their smart pill capabilities on measuring medication treatment effectiveness to improve clinical outcomes. Others, such as HQ’s CorTemp, are using the pills to monitor patients’ internal health, wirelessly transmitting data such as core temperature—measurements that can be critical in life or death situations.
IoMT is Well-Positioned for Growth
The global IoMT market was valued at $44.5 billion in 2018 and is expected to grow to $254.2 billion in 2026, according to AllTheResearch. The smart wearable device segment of IoMT, inclusive of smartwatches and sensor-laden smart shirts, made up for the largest share of the global market in 2018, at roughly 27 percent, the report finds.
This area of IoMT is poised for even further growth as artificial intelligence is integrated into connected devices and can prove capable of the real-time, remote measurement and analysis of patient data.
The IoMT ecosystem expansion is also paving the way for other new technologies, such as kiosks that provide connectivity to care providers. These kiosks will further enable clinicians to monitor and treat patients remotely—an ever-growing need for patients in rural communities, as they struggle to recruit and retain medical specialists.
Regardless of a patient’s location or condition, an evolution of the IoMT ecosystem will become increasingly impactful. And even the most remote locations will benefit from better access to care as connected medical devices continue to find their way into the hands of both patients and clinicians.
Enhancing Health and Wellness, One Device at a Time
When healthcare facilities continue to leverage IoMT, they will enhance their capabilities in treating patients and more accurately be able to provide the right diagnoses. Medtech companies must keep an eye out for further developments and continue innovating, as they have a crucial role in delivering these results to their key stakeholders.