Naomi R.
Healthcare facilities around the world are facing rising costs, exacerbated by aging populations, chronic disease, and complex care needs. The COVID-19 pandemic has not helped, either, as hospitals are frequently at full capacity.
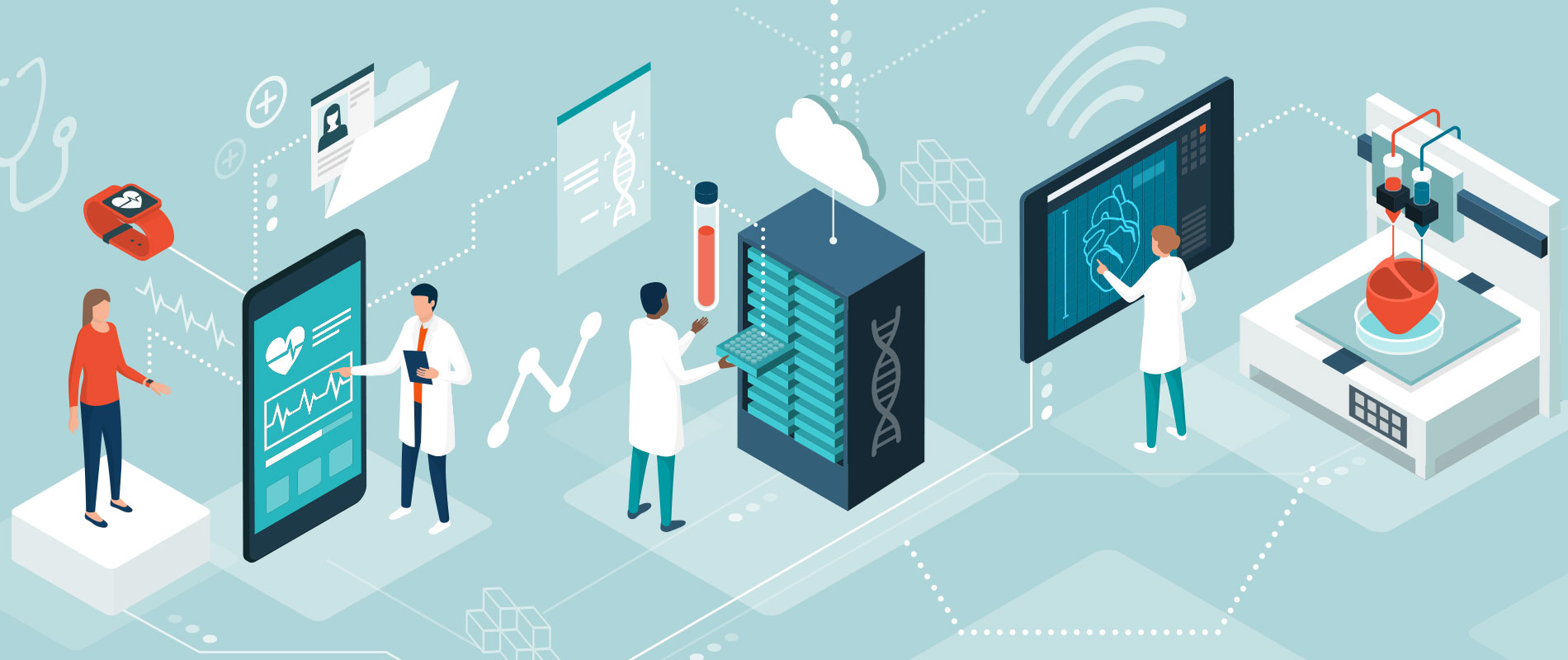
At the same time, patients are increasingly being more exposed to tech solutions to address their ailments, through advanced medical technology (MedTech) and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
How IoMT works
The proliferation of IoMT has paved the way for smart medical and platform services. These systems enable patients to send their health data to caregivers, who use the data to create a more accurate diagnosis. This minimizes the risk for errors in the prevention and treatment of disease.
A patient’s medical history is typically available within the IoMT network, which makes the work of healthcare providers (HCP) more accurate and easier. Instead of collecting the data individually, HCPs can review the history in real-time within the network. There is a minimized margin of error, not to mention a faster and more efficient workflow.
Fewer in-person visits to a doctor’s office have the potential to translate into lower medical costs. In our current environment, this also leads to a possibly minimized risk for infection, especially for vulnerable categories of populations affected by severe or chronic diseases.
The pandemic also paved the way for patients to gain access to telehealth systems. Governments and healthcare facilities sought alternatives to hospital and clinic visits, reserving those appointments for patients who most needed them.
Providing remote access to healthcare has proved popular and efficient. The virtual appointments, aided by remote tools and MedTech devices, allowed patients to be treated right away in a setting where they feel safe. Telemedicine proved to be efficient because many minor cases are dealt with faster, leaving in-person visits for more complex or serious cases. Telehealth can improve operational efficiency at the same time, as it drives up patient outcomes.
Use cases for IoMT in the age of COVID-19
Wearable biosensors were utilized at the OLVG Hospital in the Netherlands, where the devices were installed in the isolation rooms of suspected COVID-19 patients who did not require ventilation. The sensor collected data such as respiratory rate and heart rate every minute.
The same tech has been used for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), where cardiac and activity monitoring (CAM) devices track motion, environmental exposure, body temperature, and heart rate.
In addition, virtual clinics were created in the United Arab Emirates to enable access to remote care for a range of specialties. Moreover, the units were also a preventive measure to stop the spread of COVID-19.
The virtual units use smart medical devices and integrated AI solutions to provide medical services without the need for face-to-face interaction between patients and physicians.
The virtual wards or “hospitals without walls” have the potential to transform the process of caregiving. They can increase the amount of medical support provided to patients affected by chronic diseases. These clinics can also improve the percentage of people whose health is monitored on a regular basis, with the help of smart medical devices and technology, no matter where they are.
IoMT is starting to shape healthcare, thanks to its significant benefits for patients, HCPs, providers, and insurance companies. As new technologies continue to emerge, IoMT will provide enhanced access to medical care for patients around the world. Its benefits will be further realized once security and connectivity are thoroughly considered by manufacturers.